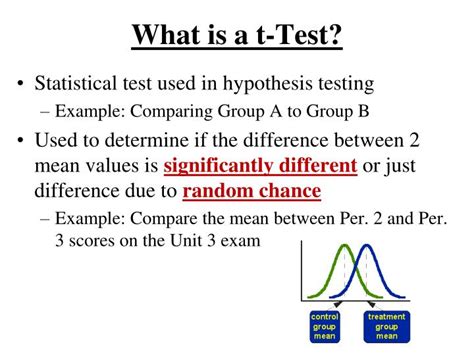
t test quantitative|statistical t test meaning : online sales The t test tells you how significant the differences between group means are. It lets you know if those differences in means could have happened by chance. The t test is usually used when . webA edição de Natal de El Gordo realiza-se apenas uma vez por ano. O sorteio desta edição de Natal de grande popularidade realiza-se no dia 22 de Dezembro de cada ano. É aí .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Se inscreva e me acompanhe no insta ️
The 1-sample t-test evaluates a single list of numbers to test the hypothesis that a statistic of that set is equal to a chosen value, for instance, to test the hypothesis that the .
The t test tells you how significant the differences between group means are. It lets you know if those differences in means could have happened by chance. The t test is usually used when .Explicit expressions that can be used to carry out various t-tests are given below. In each case, the formula for a test statistic that either exactly follows or closely approximates a t-distribution under the null hypothesis is given. Also, the appropriate degrees of freedom are given in each case. Each of these statistics can be used to carry out either a one-tailed or two-tailed test.
A t-test is an inferential statistic used in hypothesis testing to determine if there is a statistically significant difference between the means of two samples.A t-test is a tool for evaluating the means of one or two populations using hypothesis testing. Learn about types of t-tests, t-test assumptions and how to perform a t-test.
A t test is a statistical technique used to quantify the difference between the mean (average value) of a variable from up to two samples (datasets). The variable must be numeric. Some examples are height, gross income, and . This comparison can be analyzed by conducting different statistical analysis, such as t-test, which is the one described in this article. So, what is a t-test? It is a type of inferential statistic used to study if there is a statistical . Revised on June 22, 2023. Statistical tests are used in hypothesis testing. They can be used to: determine whether a predictor variable has a statistically significant relationship with an outcome variable. estimate .An introduction to statistics usually covers t tests, ANOVAs, and Chi-Square. For this course we will concentrate on t tests, although background information will be provided on ANOVAs and Chi-Square. A PowerPoint presentation on t tests .
The t-test is frequently used in comparing 2 group means.The compared groups may be independent to each other such as men and women. Otherwise, compared data are correlated in a case such as comparison of blood pressure levels from the same person before and after medication ().In this section we will focus on independent t-test only.There are 2 kinds of .
The results of the test are shown in Table 4. In t-test analysis, the effect of binary variables on the dependent variable is checked, and predictions are made, taking it criterion for the p-value . Highlights. Group Comparison: ANOVA is ideal for multiple-group comparisons, while the t-test is tailored for two-group analyses. Research Design Suitability: ANOVA suits complex designs with multiple independent variables; the t-test is used for more straightforward, single-independent variable studies. Key Assumptions: Both tests require normal distribution, .With a paired t test, the values in each group are related (usually they are before and after values measured on the same test subject). In contrast, with unpaired t tests, the observed values aren’t related between groups. An unpaired, or independent t test, example is comparing the average height of children at school A vs school B.
What is a t-test?. A t-test (also known as Student's t-test) is a tool for evaluating the means of one or two populations using hypothesis testing. A t-test may be used to evaluate whether a single group differs from a known value (a one-sample t-test), whether two groups differ from each other (an independent two-sample t-test), or whether there is a significant difference in .
Dieses Kapitel beschäftigt sich mit einem grundlegenden statistischen Verfahren zur Auswertung erhobener Daten: dem t-Test. Der t-Test untersucht, ob sich zwei empirisch gefundene Mittelwerte systematisch voneinander unterscheiden. Mit Hilfe dieses. Quantitative data is that which can be expressed numerically and is associated with a measurement scale; not all numbers constitute quantitative data (e.g. tax file number!) . Students t Test (n < 60) – can be paired (same subjects on two different variables) or unpaired (independent samples); t statistic can only be computed for 2 groups .The two sample t test estimates that the mean difference is -13.24. However, that estimate is based on 30 observations split between the two groups and it is unlikely to equal the population difference. The confidence interval indicates that the mean difference between these two methods for the entire population is likely between -19.89 and -6.59. T-TEST INDEPENDENT - https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Hcw6yO_Aq0g&list=PLKt6D8cHRaGYHahOGtFYGR4CBzI9bf9aM&index=24CORRELATION - https://www.youtube.com/watch?.
A paired t-test takes paired observations (like before and after), subtracts one from the other, and conducts a 1-sample t-test on the differences. Typically, a paired t-test determines whether the paired differences are significantly different from zero. Download the CSV data file to check this yourself: T-testData. All of the statistical . Independent samples t-test: compares the means for two groups. Paired sample t-test: compares means from the same group at different times (say, one year apart). One sample T-test. One sample t-test is one of the widely used t-tests for comparison of the sample mean of the data to a particularly given value. Used for comparing the sample mean .The results for the two-sample t-test that assumes equal variances are the same as our calculations earlier. The test statistic is 2.79996. The software shows results for a two-sided test and for one-sided tests. The two-sided test is what we want (Prob > |t|). Our null hypothesis is that the mean body fat for men and women is equal.
how to test sas hard drive dell poweredge r510
T-test definition, formula explanation, and assumptions. The T-test is the test, which allows us to analyze one or two sample means, depending on the type of t-test. Yes, the t-test has several types: One-sample t-test — compare the mean of one group against the specified mean generated from a population. For example, a manufacturer of mobile .The data are quantitative; The distribution of the differences (not the original data), is plausibly Normal. . It would seem logical that, because the t test assumes Normality, one should test for Normality first. The problem is that the . Choose the type of t-test you wish to perform: A one-sample t-test (to test the mean of a single group against a hypothesized mean); A two-sample t-test (to compare the means for two groups); or. A paired t-test (to check how the mean from the same group changes after some intervention). Decide on the alternative hypothesis: Two-tailed; Left .A/B testing compares two versions of something (e.g., website designs or marketing campaigns) to decide which performs better.. T-tests are crucial in A/B testing as they help you analyze the results and make statistically valid .
Quantitative research serves as the cornerstone of evidence-based decision-making. Its importance cannot be overstated: quantitative methods provide empirical rigor, enabling preachers (academia), practitioners (industry), and policymakers (government; i.e. the 3Ps) to derive actionable insights from data. However, despite its significance, mastering the .The Paired t-test is also known as the Paired Samples t-test or the Dependent t-test. Paired T-test Assumptions Just like in the Independent t-test from our previous chapter, there are a number of assumptions that need to be met before performing a Paired-samples t-test: This tutorial explains the difference between a t-test and an ANOVA, along with when to use each test.. T-test. A t-test is used to determine whether or not there is a statistically significant difference between the means of two groups.There are two types of t-tests: 1. Independent samples t-test. This is used when we wish to compare the difference between .
Learn how to perform one and two sample t-tests on vectors of data using the t.test function in R. When to use a t-test: To determine if a population mean is different from a known value (one-sample t-test), to compare means of two groups (independent two-sample t-test) or to compare two means of a group at different times (paired t-test). When to use a chi-square test: To compare categorical variables, such as determining whether sample data matches .Χ 2 = 8.41 + 8.67 + 11.6 + 5.4 = 34.08. Step 3: Find the critical chi-square value. Since there are four groups (round and yellow, round and green, wrinkled and yellow, wrinkled and green), there are three degrees of freedom.. For a test of significance at α = .05 and df = 3, the Χ 2 critical value is 7.82.. Step 4: Compare the chi-square value to the critical value
Quantitative Research. Quantitative research is a type of research that collects and analyzes numerical data to test hypotheses and answer research questions.This research typically involves a large sample size and uses statistical analysis to make inferences about a population based on the data collected.Step 4. Test the null hypothesis. To test the null hypothesis, A = B, we use a significance test. The italicized lowercase p you often see, followed by > or < sign and a decimal (p ≤ .05) indicate significance. In most cases, the researcher tests the null hypothesis, A = B, because is it easier to show there is some sort of effect of A on B, than to have to determine a positive or negative .The content in these areas includes high school mathematics and statistics at a level that is generally no higher than a second course in algebra. It doesn’t include trigonometry, calculus or other higher-level mathematics. The Math Review (PDF) provides detailed information about the content of the Quantitative Reasoning measure.Math: Pre-K - 8th grade; Pre-K through grade 2 (Khan Kids) Early math review; 2nd grade; 3rd grade; 4th grade; 5th grade; 6th grade; 7th grade; 8th grade; 3rd grade math (Illustrative Math-aligned)
what is a t test
Zona Leste 33 anos R$ 150. star Sexo c anal e local 170 chamada de vídeo 20 arthur alvim. Zona Leste 25 anos R$ 150. check Verificada. 511 garotas de programa na Zona Leste .
t test quantitative|statistical t test meaning